Security Best Practices When Using Cross-Chain Bridges: A Relay Protocol User Guide

Cross-chain bridges have become essential tools for navigating the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, enabling seamless asset transfers across various blockchain networks. However, their growing prominence has also made them prime targets for malicious actors. As a user of Relay Protocol—a leading platform for instant, low-cost cross-chain bridging—it's crucial to understand and implement security best practices to safeguard your assets.
Understanding the Security Landscape of Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges function by facilitating the transfer of assets between different blockchain networks. While they offer convenience, they also introduce unique security challenges. Notably, high-profile bridge hacks, such as the Ronin Bridge breach resulting in a $540 million loss, underscore the vulnerabilities inherent in these systems. Common attack vectors include smart contract exploits, compromised private keys, and phishing attacks.
Relay Protocol: A Secure Approach to Cross-Chain Transactions
Relay Protocol distinguishes itself by employing a relayer-based model, where trusted relayers execute transactions on behalf of users. This design offers several security advantages:
- Optimistic Execution: Relayers can fulfill transactions instantly, reducing exposure time to potential threats.
- Reduced On-Chain Complexity: By minimizing on-chain interactions, Relay lowers the risk of smart contract vulnerabilities.
- Transparent Operations: Users receive detailed quotes outlining fees and expected outcomes, promoting informed decision-making.
Best Practices for Secure Bridging with Relay
To maximize security while using Relay Protocol, consider the following recommendations:
1. Always Use the Official Relay Website
Phishing attacks often involve fake websites mimicking legitimate platforms. To avoid such scams:
- Bookmark and access Relay only through https://relay.link.
- Avoid clicking on links from unsolicited messages or advertisements.
- Be wary of slight misspellings in URLs, such as "relaly.link" or "relayprotocols.xyz"
2. Use Trusted Wallets and Keep Them Secure
Your wallet is your gateway to the blockchain. Ensure its security by:
- Using reputable wallets like MetaMask or Phantom.
- Regularly updating your wallet software to the latest version.
- Storing your seed phrase offline and never sharing it with anyone.
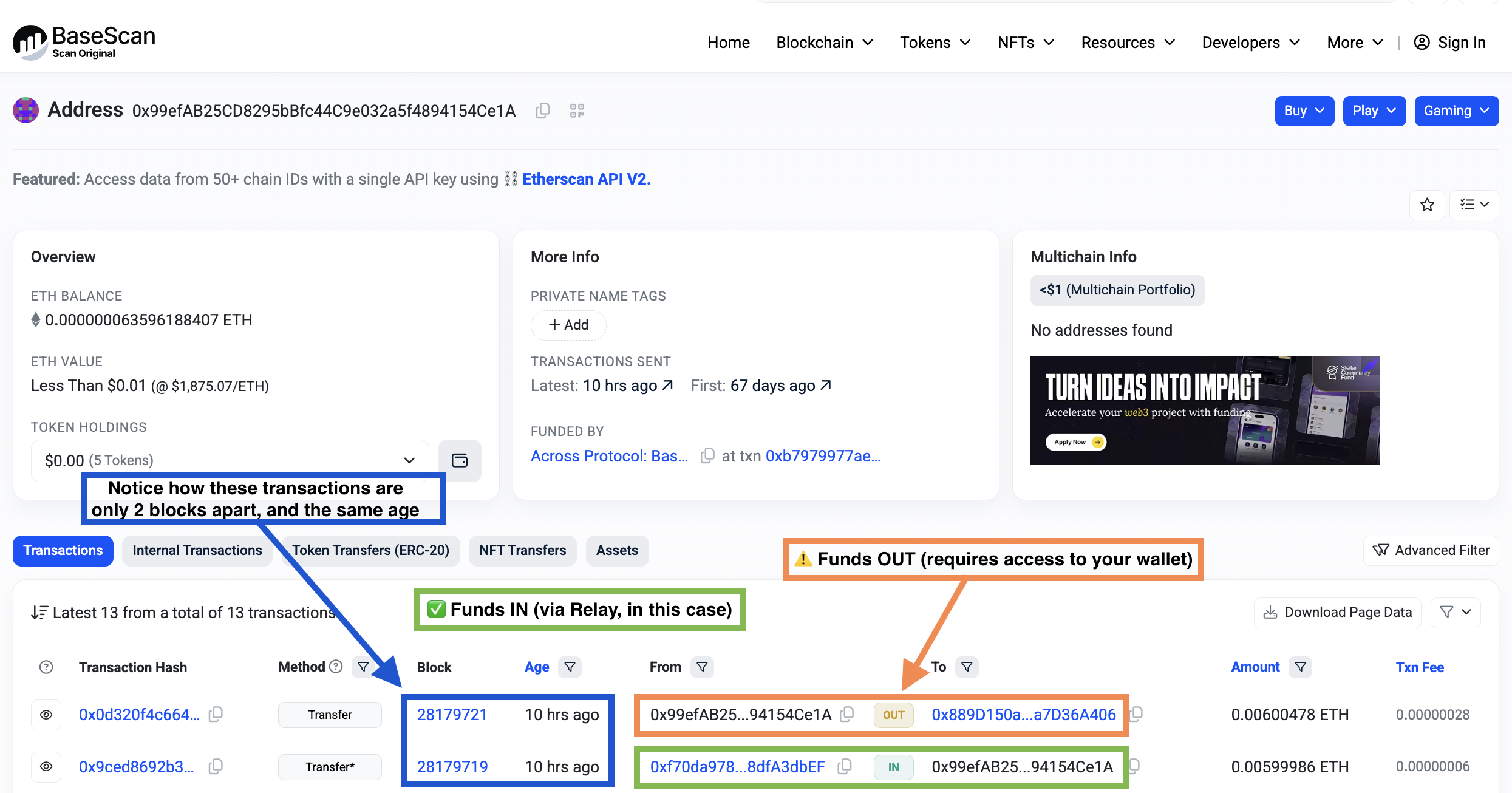
3. Monitor Transactions and Approvals
Regularly review your wallet's transaction history and revoke unnecessary approvals:
- Use tools like Revoke.cash to manage and revoke token approvals.
- Be cautious of unsolicited requests to approve transactions or connect your wallet.
4. Respond Promptly to Suspicious Activity
If you suspect your wallet has been compromised:
- Cease all activity with the affected wallet immediately.
- Transfer remaining assets to a new, secure wallet.
- Scan your device for malware and remove any suspicious applications or extensions.
- Review Relay's comprehensive guide on compromised wallets for detailed steps.
Staying Informed and Vigilant
The security landscape in DeFi is continually evolving. Stay ahead by:
- Following Relay's official channels for updates and security advisories
- Educating yourself on common scams and how to avoid them
- Engaging with the community to share experiences and learn from others
By adhering to these best practices, you can navigate the world of cross-chain bridging with greater confidence and security. Relay Protocol's commitment to user safety, combined with your proactive measures, creates a robust defense against potential threats
For more information and resources, visit Relay Radar.
