Cross-Chain vs. Same-Chain Swaps: When to Use Each and How Relay Optimizes Both

Understanding whether to use cross-chain swaps or same-chain swaps can significantly impact transaction costs, speed, and overall efficiency. This comprehensive guide will explore both swap types, help you determine which is right for your specific needs, and highlight how Relay optimizes these experiences for maximum efficiency and minimal cost.
Understanding Same-Chain Swaps: The Foundation of Token Exchange
Same-chain swaps (also known as standard swaps) refer to the exchange of tokens that exist within the same blockchain network. These are the most common and straightforward type of cryptocurrency exchanges that most users encounter when first entering the space.
How Same-Chain Swaps Work
When performing a same-chain swap, you're essentially exchanging one token for another on the same blockchain. For example, swapping ETH for USDC on the Ethereum network, or SOL for a Solana-based token on the Solana blockchain. These transactions utilize decentralized exchanges (DEXs) through liquidity pools or order books maintained within that single blockchain ecosystem.
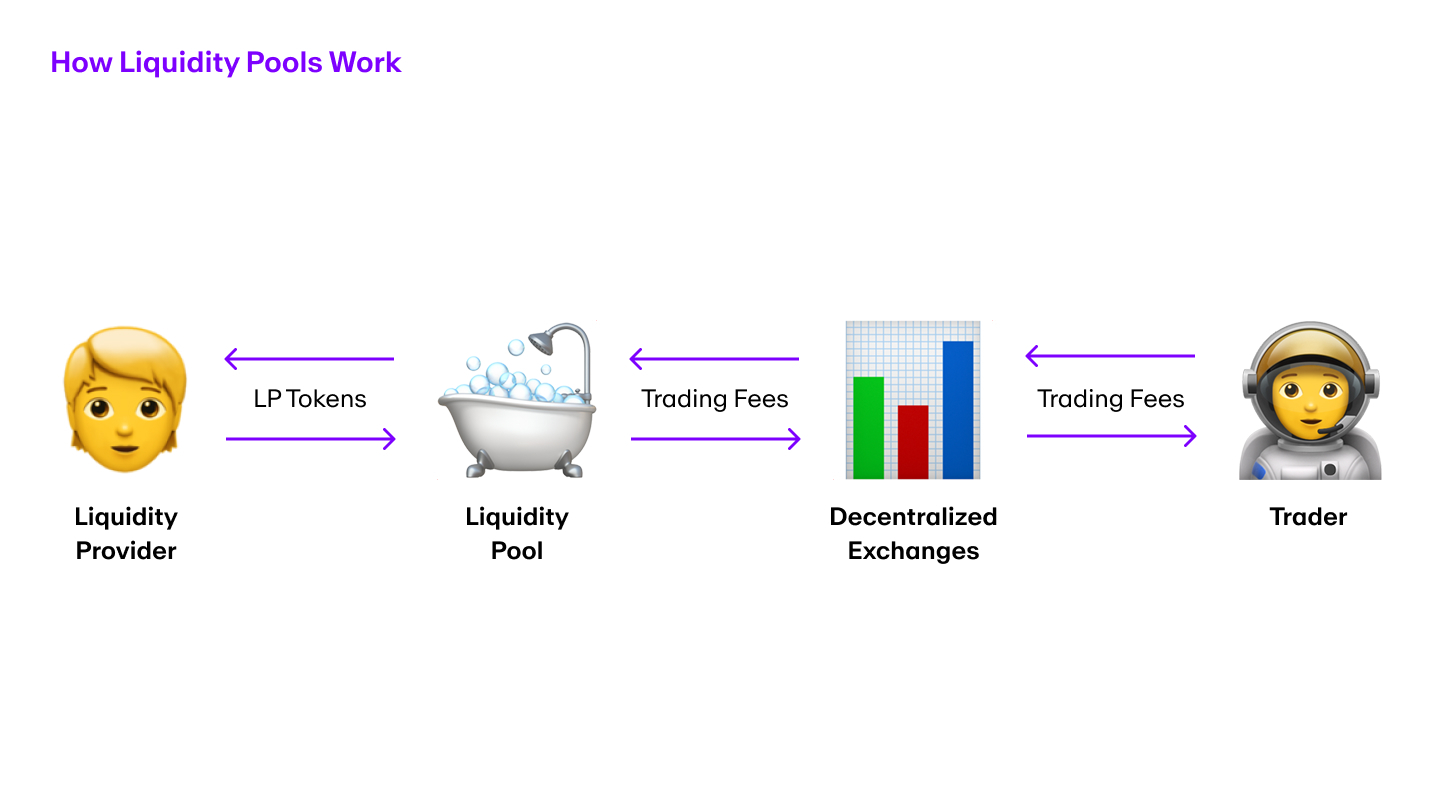
Advantages of Same-Chain Swaps
Same-chain swaps offer several notable benefits:
- Simplicity: The technical complexity is significantly lower as there's no need to coordinate between different blockchain protocols.
- Speed: Transactions typically complete within a single block confirmation time of the native blockchain.
- Lower technical complexity: Users don't need to understand multiple blockchain systems or navigate cross-chain compatibility issues.
- More mature infrastructure: Same-chain DEXs and trading platforms have been around longer and typically offer more refined user experiences.
- Deeper liquidity: Trading pairs within the same blockchain often have better liquidity, resulting in less slippage for larger trades.
Limitations of Same-Chain Swaps
Despite their advantages, same-chain swaps have certain constraints:
- Limited trading options: Users can only access tokens available on that specific blockchain.
- Network congestion effects: During high traffic periods on popular networks like Ethereum, transaction costs can spike dramatically.
- Ecosystem isolation: Users remain locked within a single blockchain ecosystem, unable to leverage opportunities on other networks without additional steps.
Cross-Chain Swaps: Breaking Down Blockchain Barriers
Cross-chain swaps represent a significant advancement in blockchain technology, enabling the direct exchange of cryptocurrencies between different blockchain networks without relying on centralized intermediaries. This breakthrough technology has transformed how users interact with the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
How Cross-Chain Swaps Work
Cross-chain swaps utilize sophisticated mechanisms to ensure secure asset exchange between disparate blockchain networks. One of the most common implementations uses Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs), which lock assets in smart contracts until specific conditions are met within a predetermined timeframe.
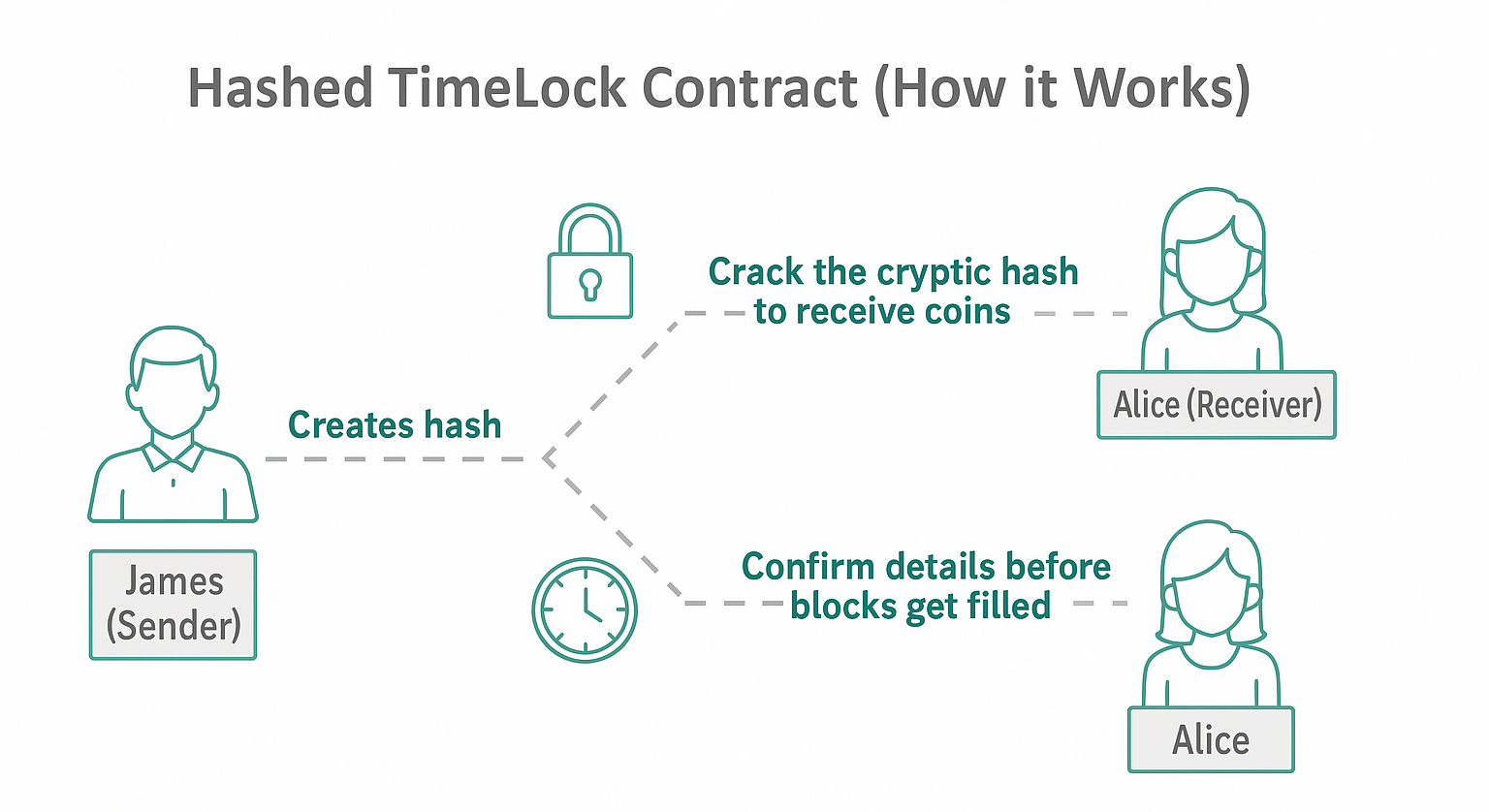
The process typically follows these steps:
- Initiation: Parties define the conditions of the swap and determine what assets will be exchanged.
- Commitment: Assets are locked in smart contracts on their respective blockchains, with cryptographic conditions ensuring transaction security.
- Verification: Both parties verify the transaction details and smart contract requirements.
- Execution: When conditions are met, the swap executes, releasing assets to the intended recipients on their respective chains.
- Safety mechanisms: If the swap fails to complete, time-lock features ensure assets return to their original owners.
Advantages of Cross-Chain Swaps
Cross-chain swaps offer numerous benefits that have made them increasingly popular:
- Enhanced portfolio diversification: Users can access tokens across multiple blockchain ecosystems without relying on centralized exchanges.
- Non-custodial transactions: Users maintain control of their private keys throughout the swap process.
- Increased security: When implemented correctly, cross-chain atomic swaps eliminate intermediary risks like exchange hacking.
- Lower costs over time: While sometimes more expensive initially, cross-chain swaps can save money by eliminating multiple transaction fees and exchange charges.
- Greater market access: Users can tap into opportunities across the entire cryptocurrency landscape, regardless of which blockchain they originated on.
Limitations of Cross-Chain Swaps
Despite their advantages, cross-chain swaps face several challenges:
- Technical complexity: The underlying technology requires coordination between different blockchain protocols, which can be technically challenging.
- Limited network support: Not all blockchains support cross-chain functionality, restricting available trading pairs.
- Liquidity concerns: Cross-chain liquidity pools may have less depth than their same-chain counterparts, potentially resulting in higher slippage.
- Speed limitations: Cross-chain swaps typically take longer to execute than same-chain alternatives due to the need to coordinate confirmations across multiple networks.
When to Use Same-Chain vs. Cross-Chain Swaps
Choosing between same-chain and cross-chain swaps depends on several key factors:
Choose Same-Chain Swaps When:
- You're exchanging tokens that exist on the same blockchain
- Transaction speed is your primary concern
- You want to minimize complexity and potential points of failure
- The trading pair has excellent liquidity within the same blockchain
- You're a beginner looking for the simplest trading experience
- Gas costs on your blockchain of choice are currently low
Choose Cross-Chain Swaps When:
- You need to exchange tokens that exist on different blockchains
- You want to avoid using centralized exchanges
- You're looking to access new opportunities on other blockchain ecosystems
- You're trying to minimize overall costs for moving between ecosystems
- You value maintaining self-custody throughout the entire process
- You're willing to accept slightly longer transaction times for greater flexibility
How Relay Optimizes Both Swap Types
Relay stands out as a versatile solution that optimizes both same-chain and cross-chain transactions, providing users with a seamless experience regardless of which approach they choose.
Relay's Cross-Chain Execution Capabilities
Relay enables powerful cross-chain functionality through its innovative relaying model. The platform facilitates low-cost, low-latency cross-chain transactions that typically complete in just 1-10 seconds. This is achieved through a unique approach:
- Cross-chain relaying model: When users want to perform cross-chain actions, they submit the necessary call data to get quotes from relayers.
- Direct transfers: Asset transfers in Relay occur directly between users and relayers, eliminating the inefficiencies of routing through complex AMMs or liquidity pools.
- Optimistic execution: Transactions are executed optimistically by a single relayer, allowing for extremely fast confirmation times.
- Strategic fee structure: Relay minimizes gas costs by splitting cross-chain transactions into components and processing validation and fee collection on cheaper settlement layers.
Relay's Same-Chain Optimization
While the search results focus primarily on Relay's cross-chain capabilities, the platform also optimizes same-chain transactions:
- Efficient liquidity sourcing: Relay sources liquidity efficiently from DEXes to provide aggregated quotes for same-chain swaps.
- Fee reduction strategies: Same-chain swaps benefit from Relay's approach to minimizing gas costs.
- Seamless user experience: The platform provides a consistent interface whether users are performing same-chain or cross-chain transactions.
Why Relay Stands Out
Relay's approach offers several advantages that make it particularly valuable for users navigating between same-chain and cross-chain swaps:
- Versatility: Supports both swap types through a single interface, eliminating the need to use different platforms
- Cost efficiency: Drastically reduces fees by performing asset exchanges off expensive chains
- Speed: Delivers fast transaction finality for both same-chain and cross-chain operations
- Arbitrary execution: Allows users to execute any action on supported chains, not just token swaps
- Integration options: Works with custom call methods or pre-defined methods from the Reservoir Aggregator
Real-World Use Cases: Choosing the Right Swap Type
Understanding real-world scenarios can help clarify when to use each swap type:
Scenario 1: Trading Popular Tokens on Ethereum
If you're looking to swap ETH for USDC on Ethereum, a same-chain swap makes perfect sense. The transaction completes quickly, and Relay optimizes the process by aggregating liquidity from multiple sources to get you the best rate.
Scenario 2: Accessing Solana-Based Applications with Ethereum Assets
If you hold ETH but want to participate in a Solana-based application, you'll need a cross-chain swap. Relay makes this seamless by handling the complex cross-chain mechanics behind the scenes, allowing you to focus on your investment strategy rather than technical details.
Scenario 3: NFT Purchases on Different Chains
If you want to purchase an NFT on Ethereum using funds from your Solana wallet, Relay's cross-chain execution capabilities make this possible without first moving to a centralized exchange. The platform can execute the necessary calldata on the destination chain after receiving your funds.
Scenario 4: Diversifying a Single-Chain Portfolio
If you've built a portfolio entirely on one blockchain but want to diversify across multiple ecosystems, cross-chain swaps provide a direct path without surrendering custody to centralized platforms. Relay's efficient cross-chain execution makes this process cost-effective and user-friendly.
The Future of Swap Technology
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, we can expect several developments in the swap landscape:
- Increased interoperability: Projects like Relay will continue improving cross-chain capabilities, making blockchain boundaries increasingly transparent to end users.
- Lower costs: Innovations in layer-2 solutions and optimistic execution models will further reduce the cost gap between same-chain and cross-chain swaps.
- Improved user experiences: Interfaces will become more intuitive, abstracting away the technical complexity of cross-chain operations.
- Greater adoption: As barriers between blockchain ecosystems fall, we'll see increased adoption of cross-chain swapping as a standard practice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Whether you should use a same-chain or cross-chain swap depends entirely on your specific needs, priorities, and the assets involved. Same-chain swaps excel in simplicity and speed but limit you to a single ecosystem. Cross-chain swaps offer greater flexibility and access but may involve more complexity.
Platforms like Relay are bridging this gap by optimizing both approaches, giving users the best of both worlds. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each swap type and leveraging tools like Relay that are designed to handle both efficiently, you can make informed decisions that maximize your opportunities in the evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
The next time you're preparing to swap tokens, consider not just the immediate transaction but your broader goals. Are you looking for the fastest possible exchange, or do you need access to a different blockchain ecosystem? With solutions like Relay, you no longer have to choose between efficiency and flexibility – you can have both.
